Vicia bithynica, commonly known as Bithynian vetch, is a perennial leguminous species belonging to the Fabaceae family, characterised by its climbing stems, which can reach about 60 centimetres above ground.
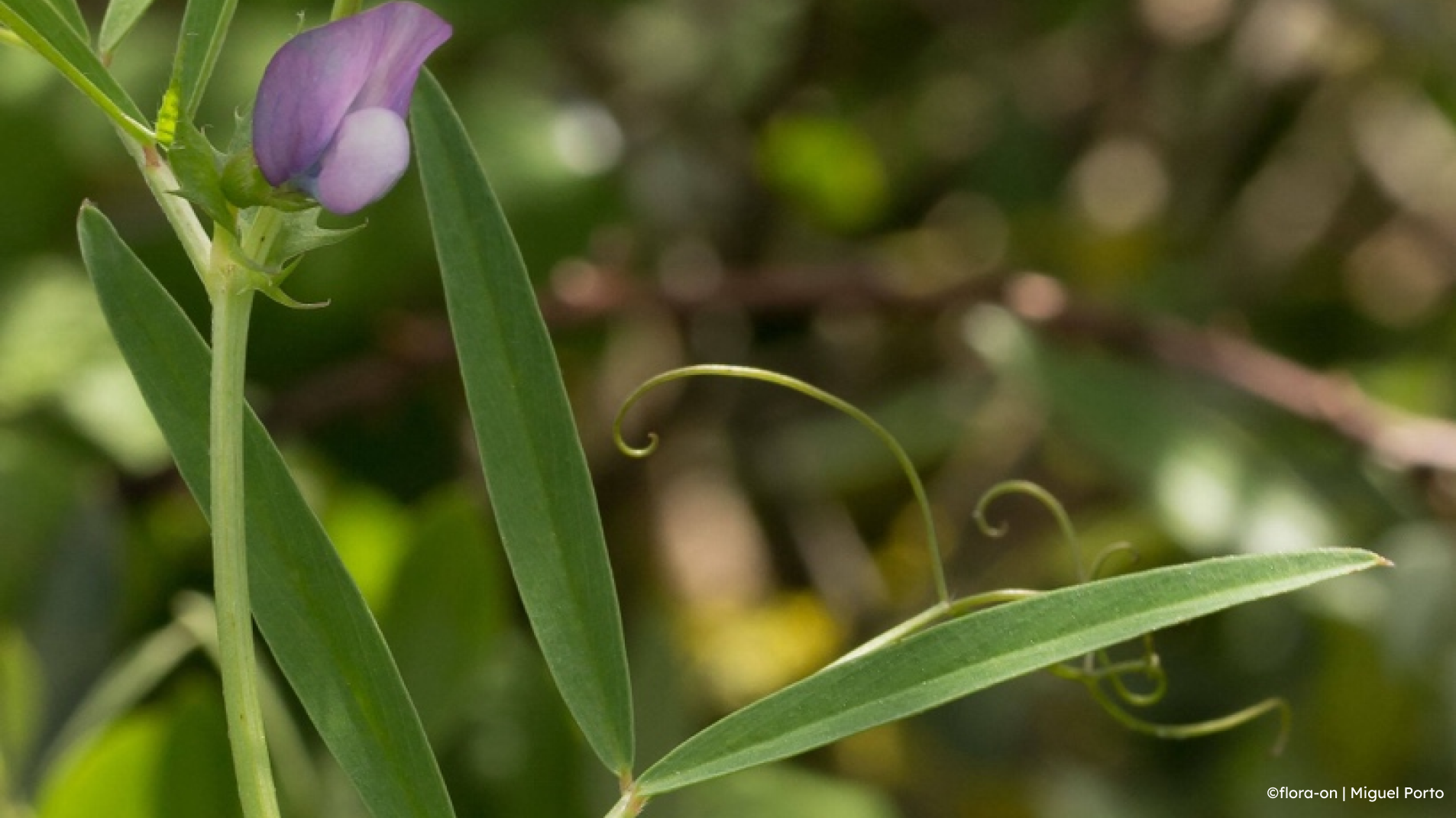
The leaves are arranged alternately along the stem and can reach up to nine centimetres in length. They have two to three pairs of leaflets and end in branched tendrils, which aid the plant in anchoring itself and “climbing”. Its petioles are about two centimetres long with a large, ovate, dentate stipule at the base.
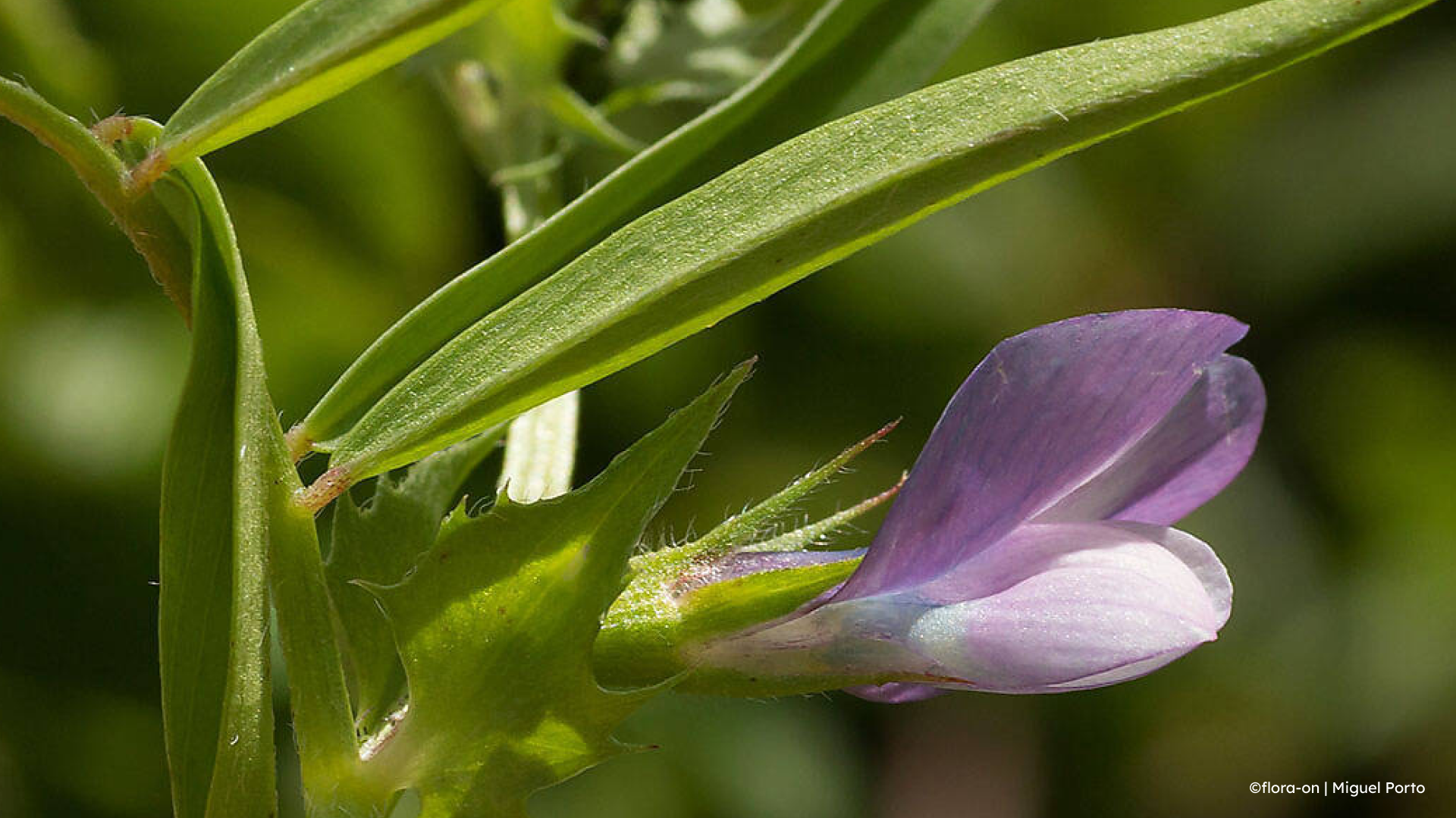
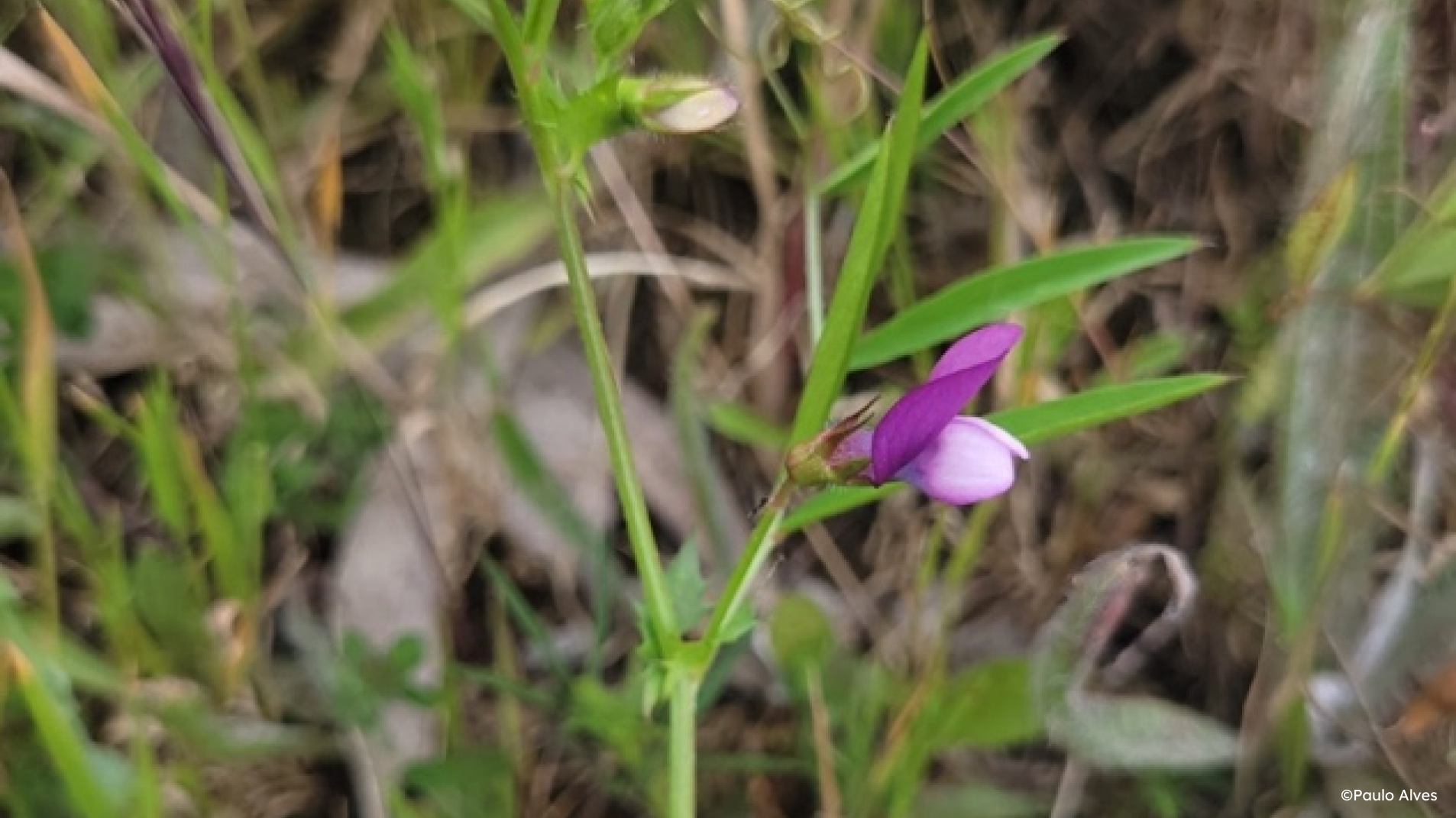
The flowers are generally arranged in pairs — although sometimes solitary — on long peduncles, with about five centimetres, branching from the leaf axils. The petals are purple and white, measuring about two centimetres in length, with a typical legume structure, and have ten stamens and one style.
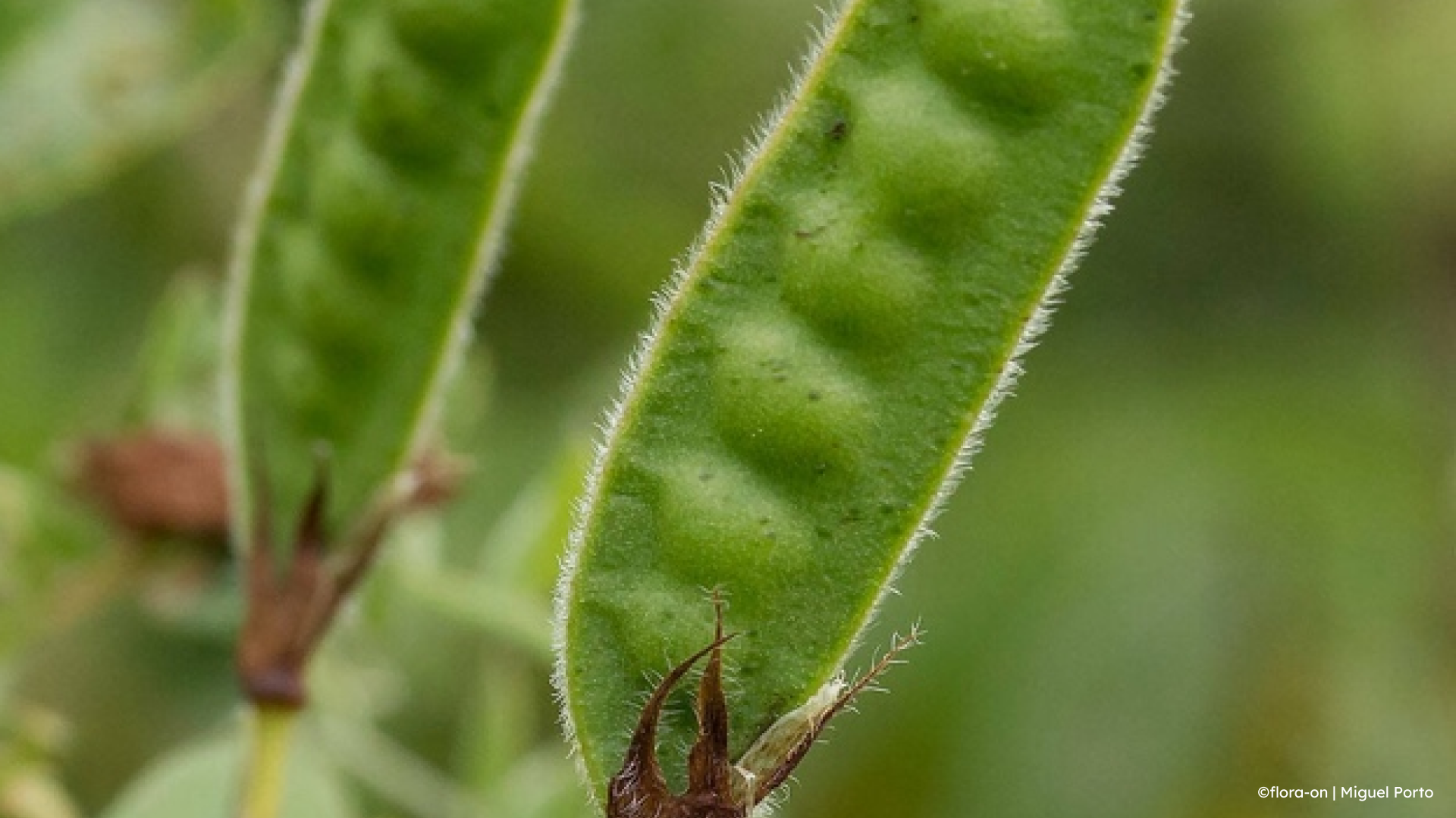
The fruit of the Bithynian vetch is a hairy pod, similar to its “cousin” the pea, measuring up to five centimetres in length and with four and eight seeds. The species has fourteen chromosomes.