The common oak (Quercus robur), also known as the European oak or English oak, is native to temperate climates on the Atlantic coast and is thought to have existed in Portugal for several thousand years. Today it is found mainly in the north and centre of the country.
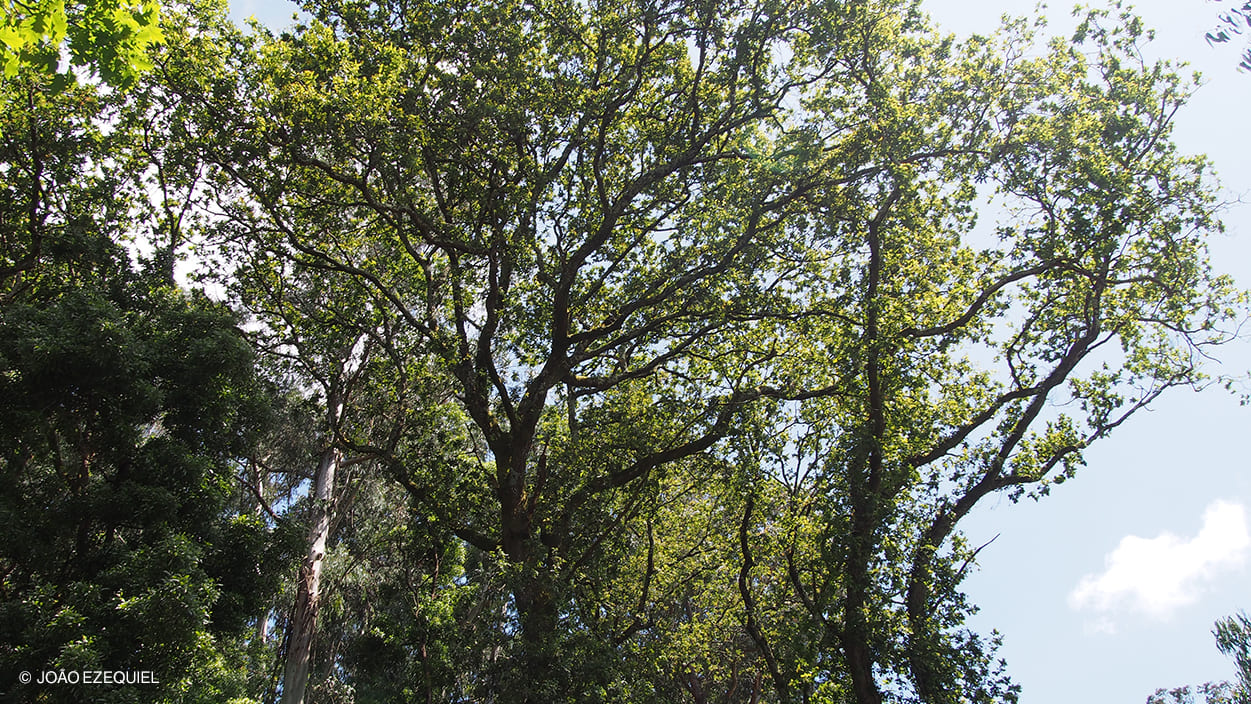
The common oak is a leafy tree that can reach 40 metres in height and grows faster than other oaks, preferring deep soil with a good level of humidity. Its crown is wide and rounded, and the deciduous leaves, which are vibrant green, grow alternately on both sides of the stem. They are thin, resistant, flexible (membranaceous), and short-stalked. The bark covering the trunk and branches is a greyish colour, which gets darker with age and has deep longitudinal grooves.
The scientific name—robur, or solid hardwood—is fitting for the wood of this tree. This high quality wood is much sought after in civil and naval construction; for the production of solid furniture; in the arts, for carving and sculpture; and also in viniculture for wine barrels. This is one of the types of wood used for ageing the famous Port wine.
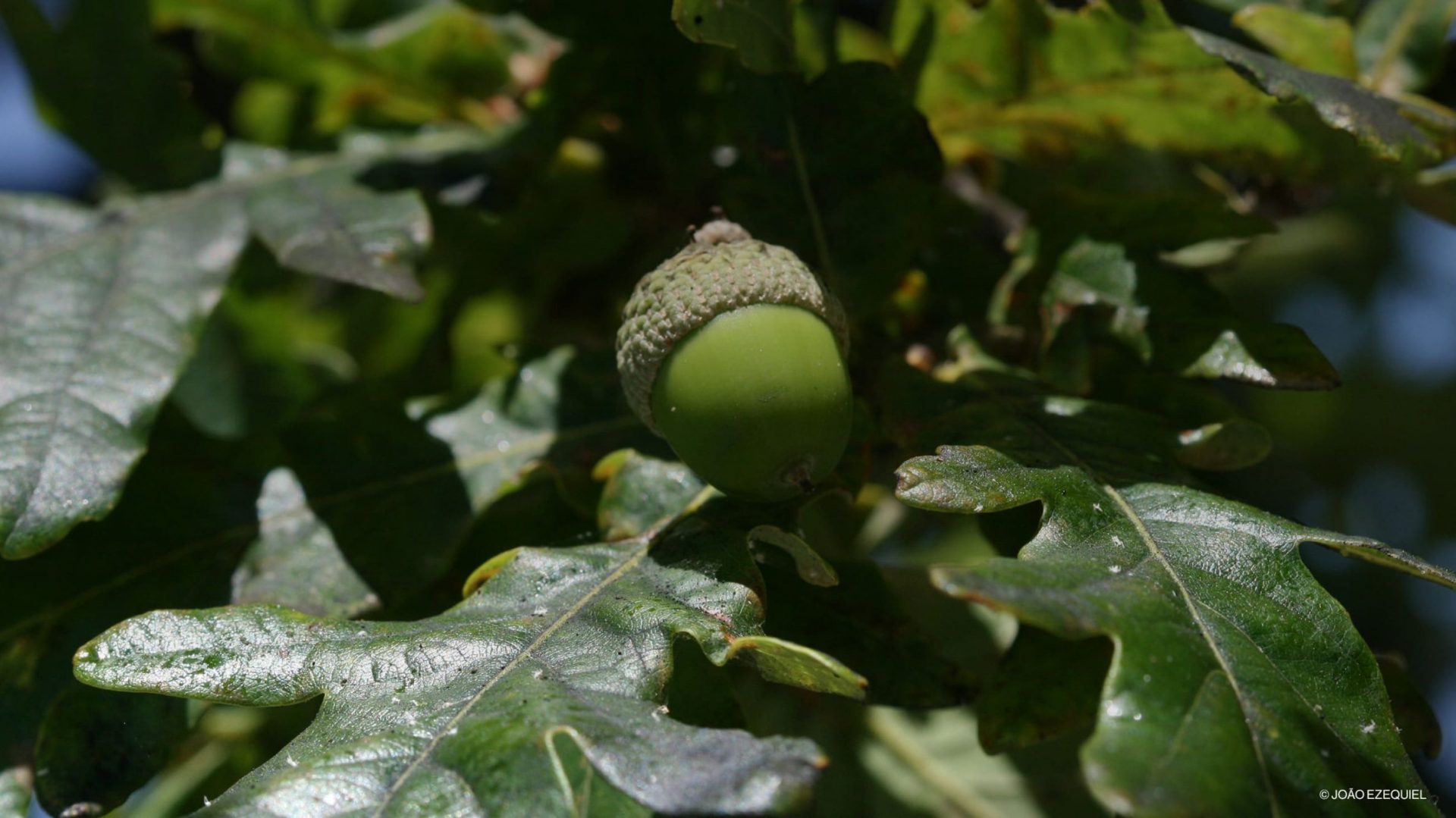
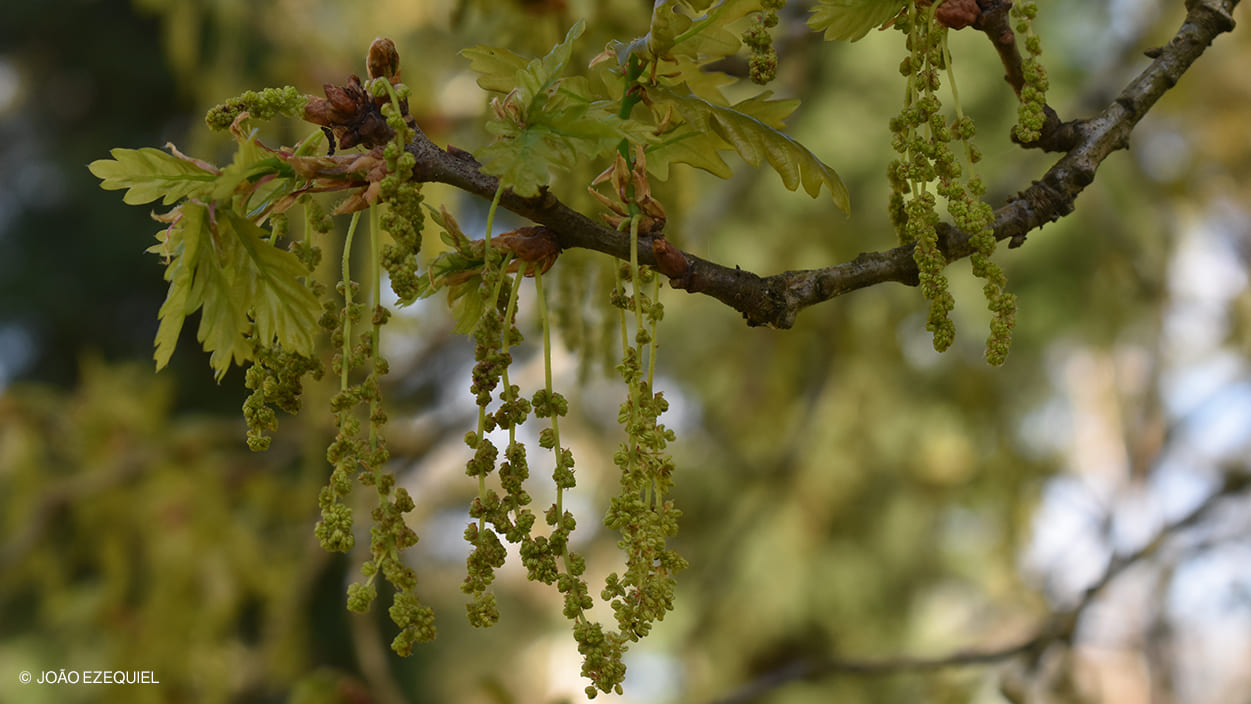
The species flowers in spring (between March and May) in inflorescences, groups of flowers that resemble clusters (catkins): the males are slender and pendulous, with many small flowers; and the females are smaller and rounder, with two to three flowers and a scaly shell. The fruit (and seed), the acorn, appears after a tree is 40 years old, reaching its maximum quality from the age of 120. It is harvested in September-October.
The common oak provides a habitat for countless species, firstly for the insects that find shelter and food on it, either in the bark or the acorn, the leaf or the roots, which, in turn, serve as food for various species of birds, such as the jays, which help with the task of pollination. Its acorns also feed various mammals, from squirrels to wild boar.
Several habitats where the common oak is predominant are included in the Natura 2000 Network Sectoral Plan: Galicio-Portuguese oak forests of Quercus robur and Quercus pyrenaica (9230pt1); pedunculated oak forests or mixed forests of sub-Atlantic and mid-European Carpinion betuli (9160pt1); and mixed forests of Quercus robur, Ulmus laevis, Ulmus minor, Fraxinus excelsior or Fraxinus angustifolia, from the banks of large rivers (habitat 91F0).