As this is one of the longest cultivated fruit trees in Europe, it’s only natural that there is so much to say about the walnut tree (Juglans regia). In addition to being highly appreciated for providing quality wood for furniture, its cultivation serves the production of well-known walnuts, used in food, but also in medicinal applications e.g. through its leaves.
You probably didn’t know that walnut plantation dates back 8,000 years. It is believed that this tree was planted for the first time in Ancient Greece and that it is native to the Mediterranean basin and central Asia. In fact, pollen and bark records show signs of cultivation in Italy about six thousand years ago and in Anatolia, Greece and Croatia about four thousand years ago, namely in farmlands, bordering cultivated fields, mudflats, vegetable gardens and orchards.
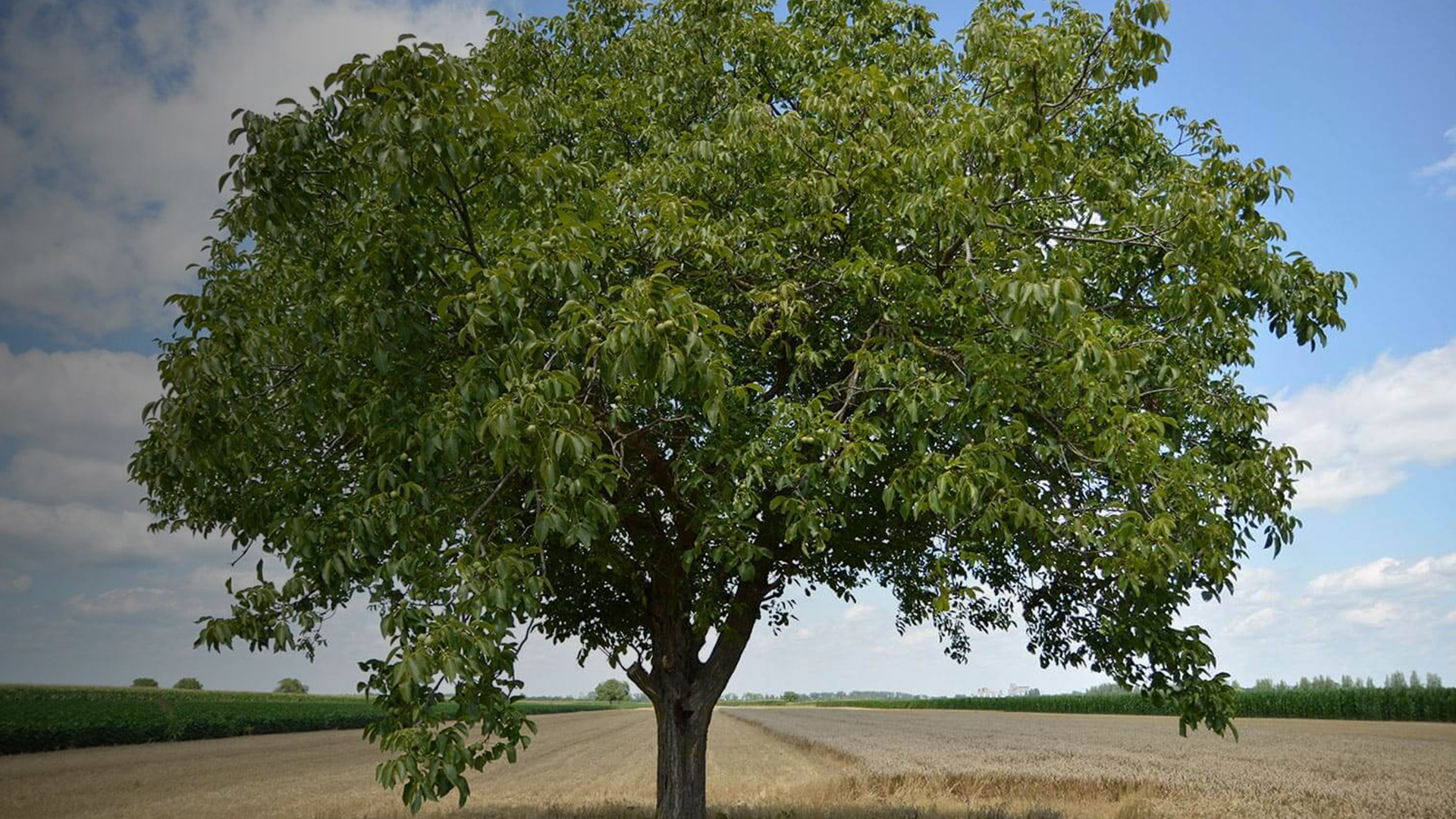
With a big capacity to adapt, this species can grow in different types of soils, although it grows more quickly in places sheltered from strong winds and high temperatures, which may burn its trunk. As regards its shape and size, it is a deciduous tree with a wide and branched canopy, which can reach 30 meters in height and last about 300 years.
Given this tree’s excellent quality wood that is easy to polish, it has been widely used in the manufacture of furniture, at least since the 16th century, but also to make musical instruments, among other objects. However, to get here this tree requires about 50 years of good management from an early age and this includes several formative cuts and pruning. The goal is to achieve a trunk without defects, with five to six meters.
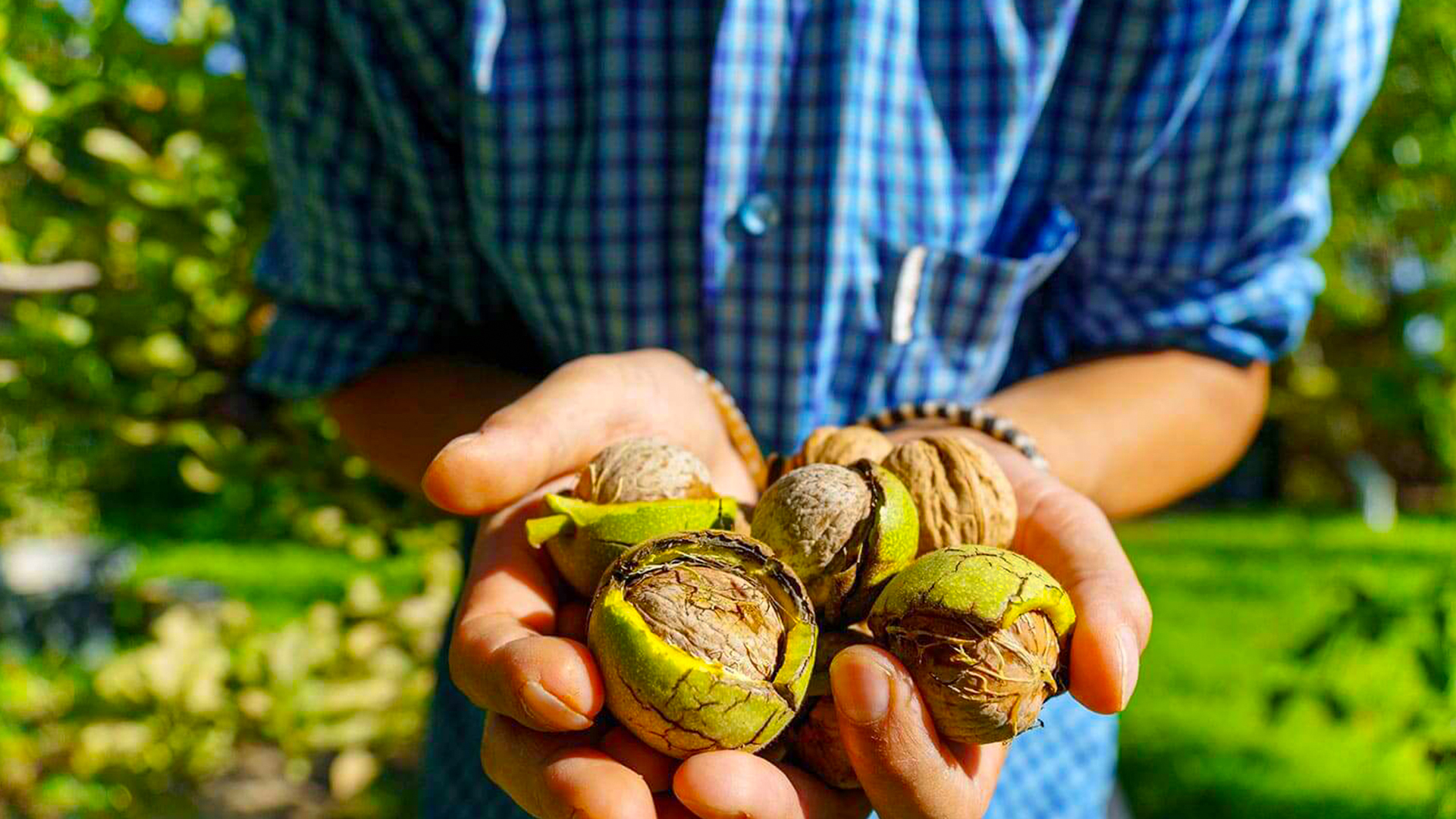
When it comes to cultivation for walnut production purposes, the walnut tree begins to bear fruit around the age of 7, increasing the quantity as it grows. That is, a 10-year-old tree can produce about five kilograms, doubling this amount when it reaches the age of 20 years and by the time it reaches between 30 and 50 years of age the maximum amount is 18 kg/tree.