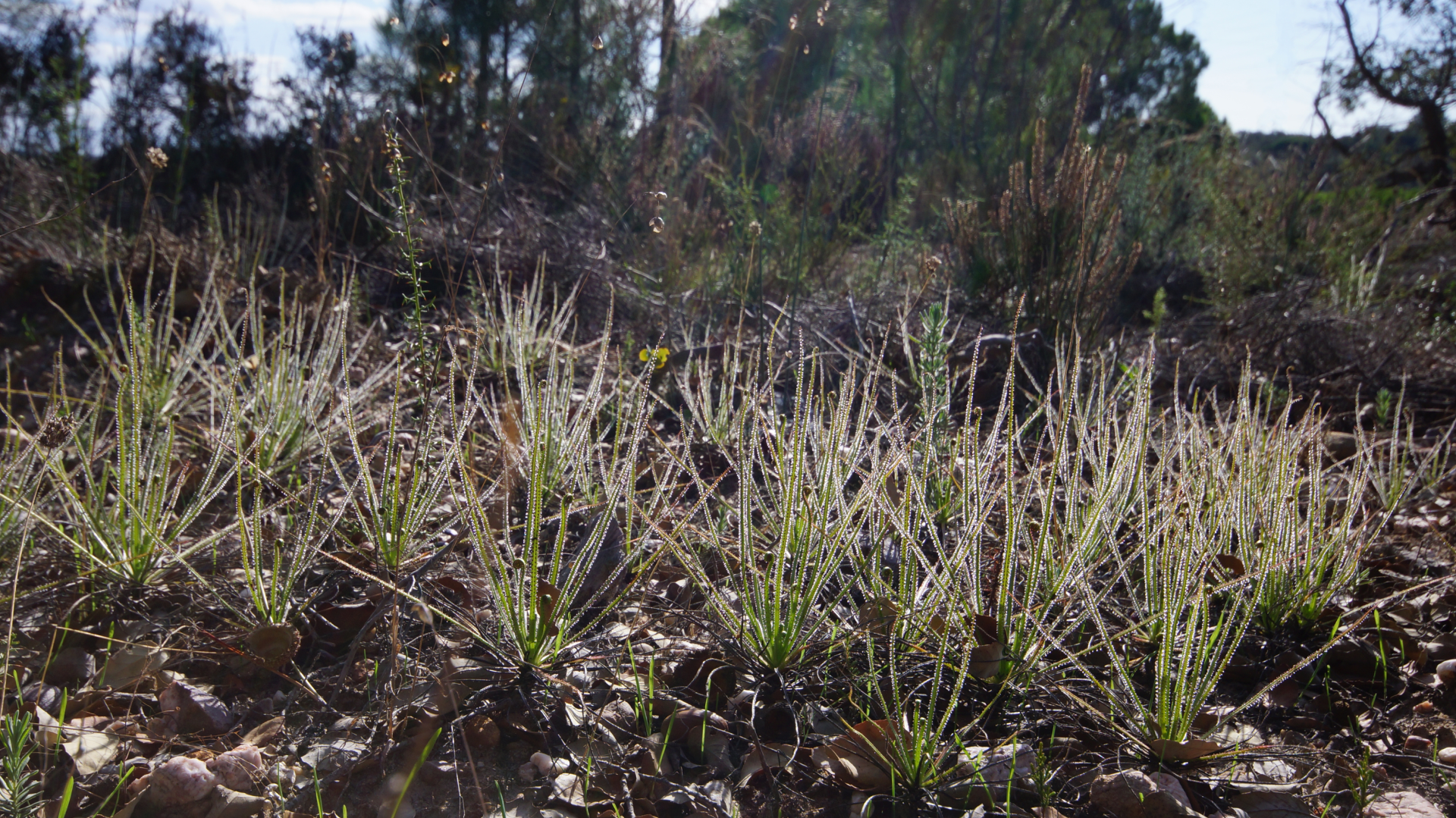
This species occurs naturally only in Portugal, Spain and North Morocco. Of all these places, Portugal is the country where this plant is much more widespread, growing all over the national territory.
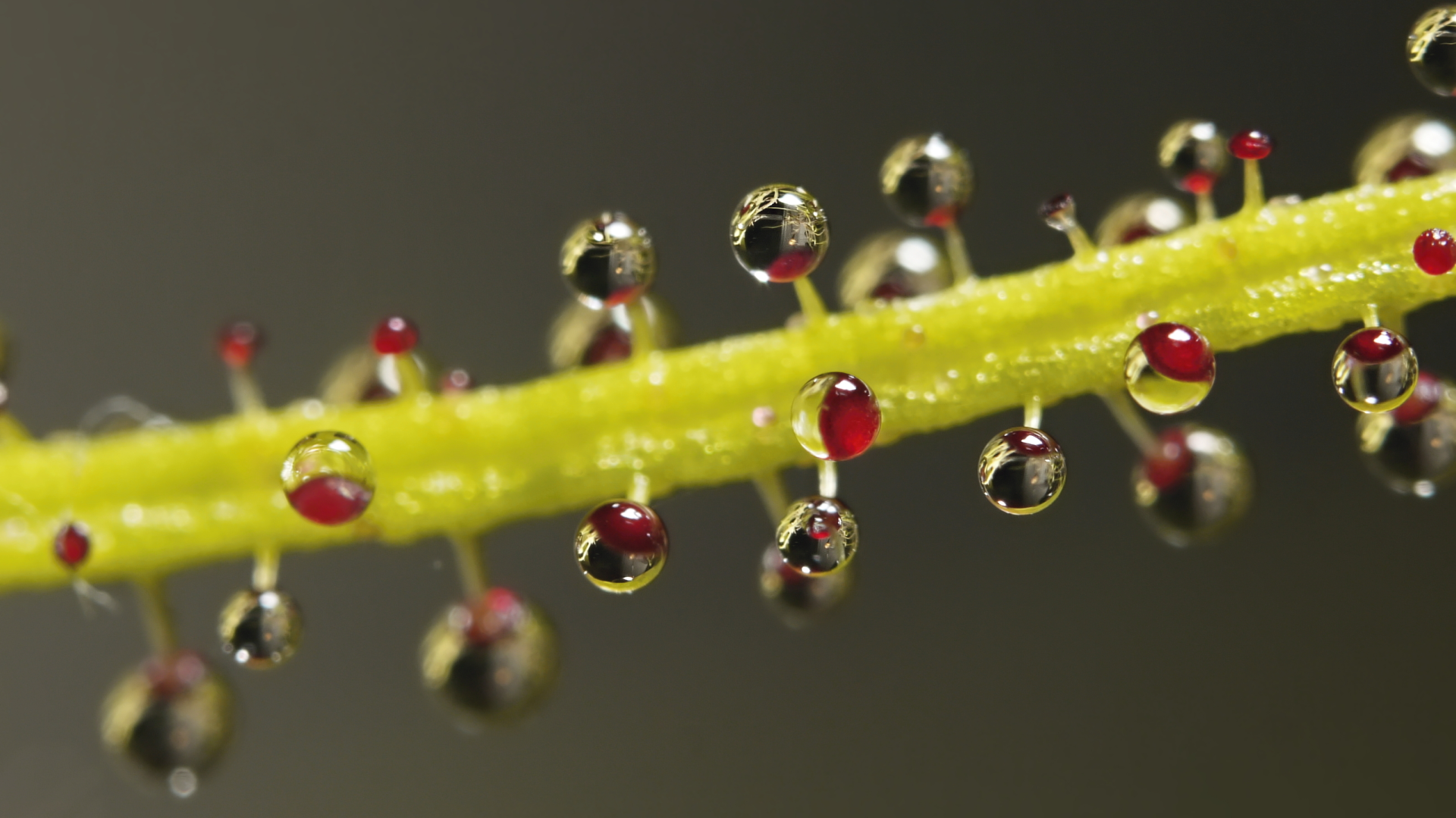
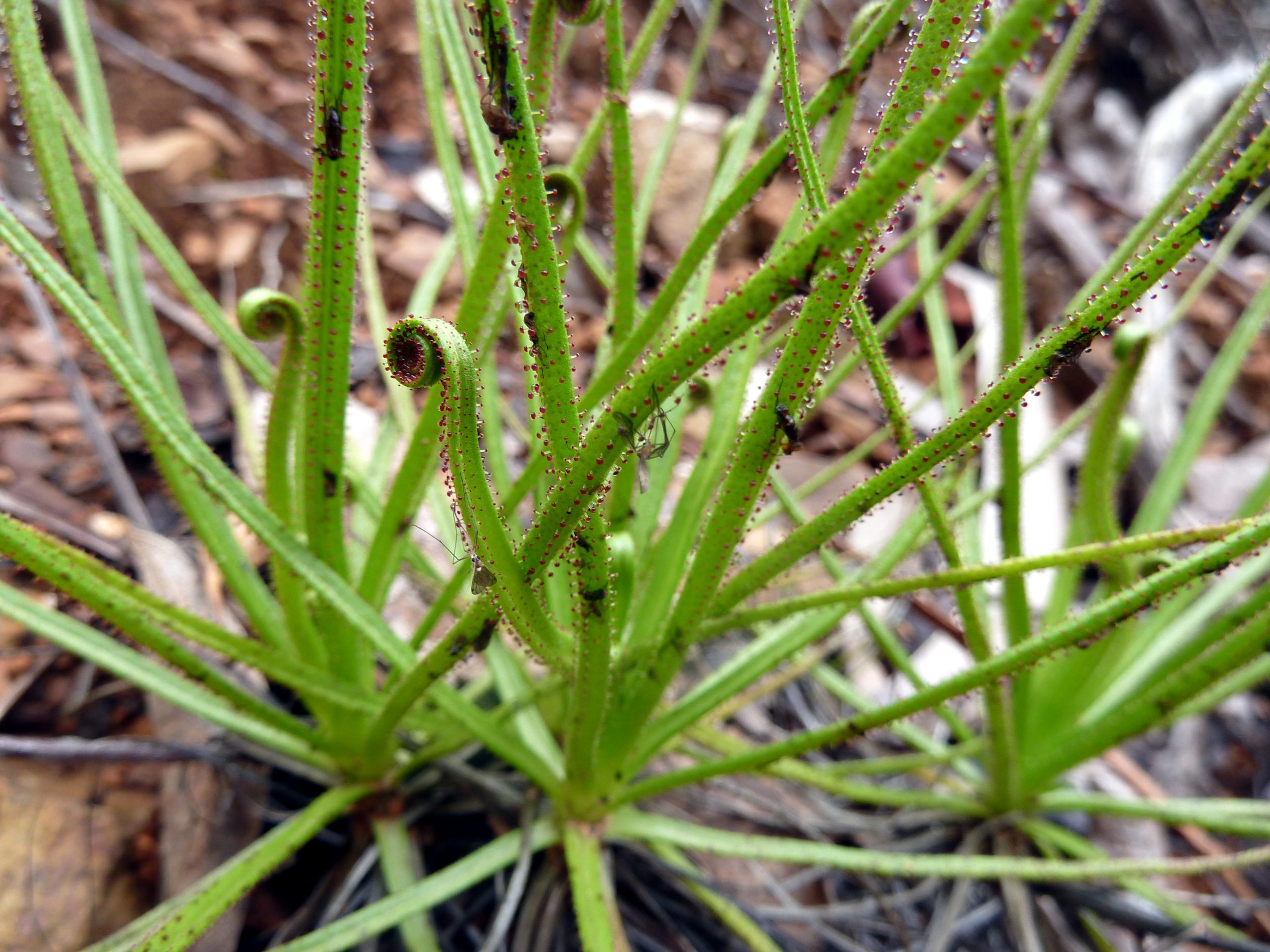
It is usually found in hard environments, such as sandy and/or dry places, forest clearings (heaths), heathlands and pine forests. This plant survives given its feeding method and the huge length of its roots, which have large ramifications. However, albeit resilient, the dewy pine is very sensitive, mostly its roots. Any type of disturbance can be lethal.
Flowering occurs during Spring resulting in bright yellow flowers with an open capsule at the top containing up to 10 black seeds.
The dewy pine is classified as vulnerable to extinction in mainland Portugal, according to the IUCN criteria.
This classification derives from the fact that the national population of this carnivorous plant does not exceed 2,500 individuals and is in a continuous decline.
There are around 600 species of carnivorous plants worldwide, classified into 14 different genera. In Portugal, it’s one of the 8 native carnivorous plants.