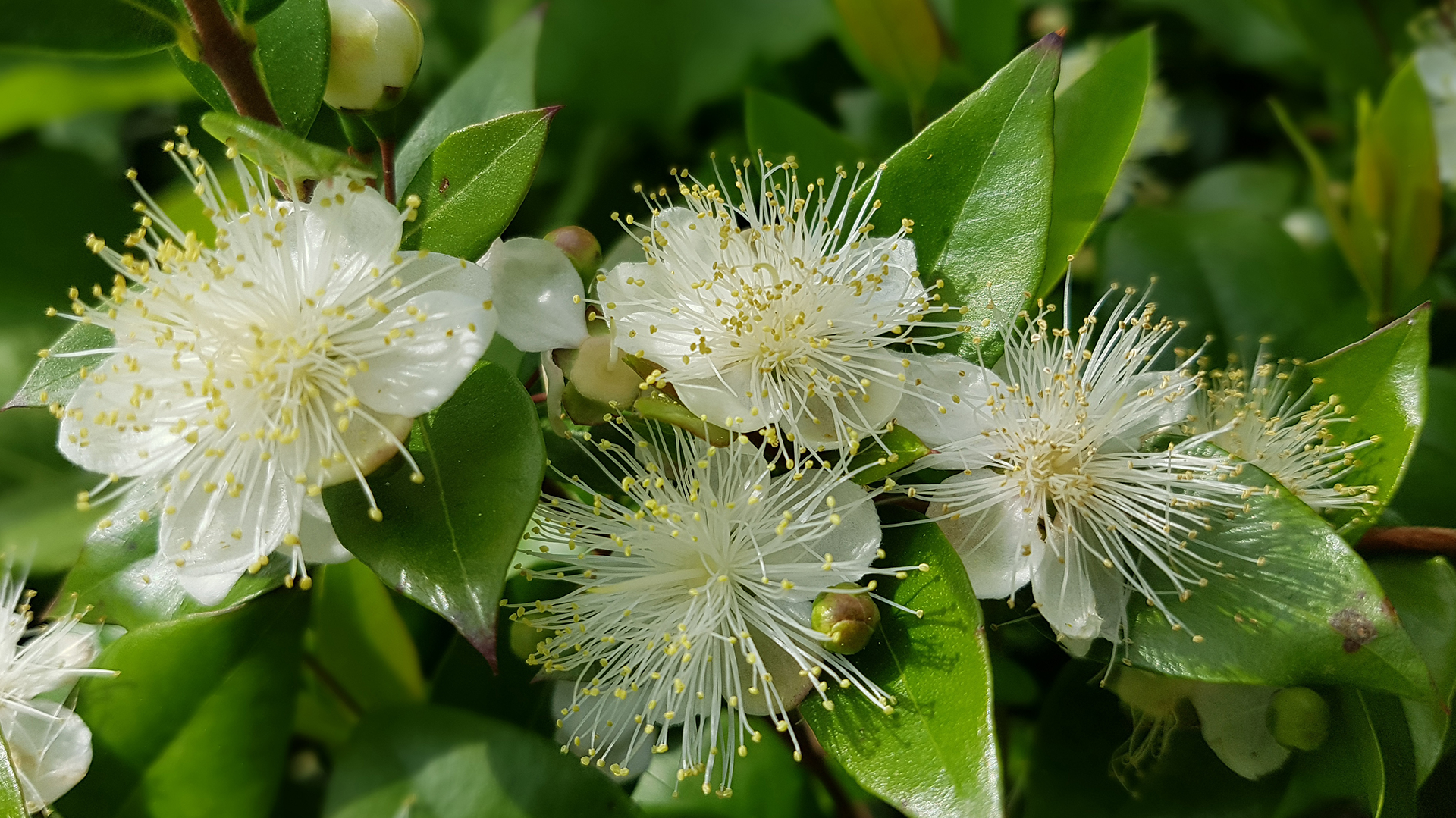
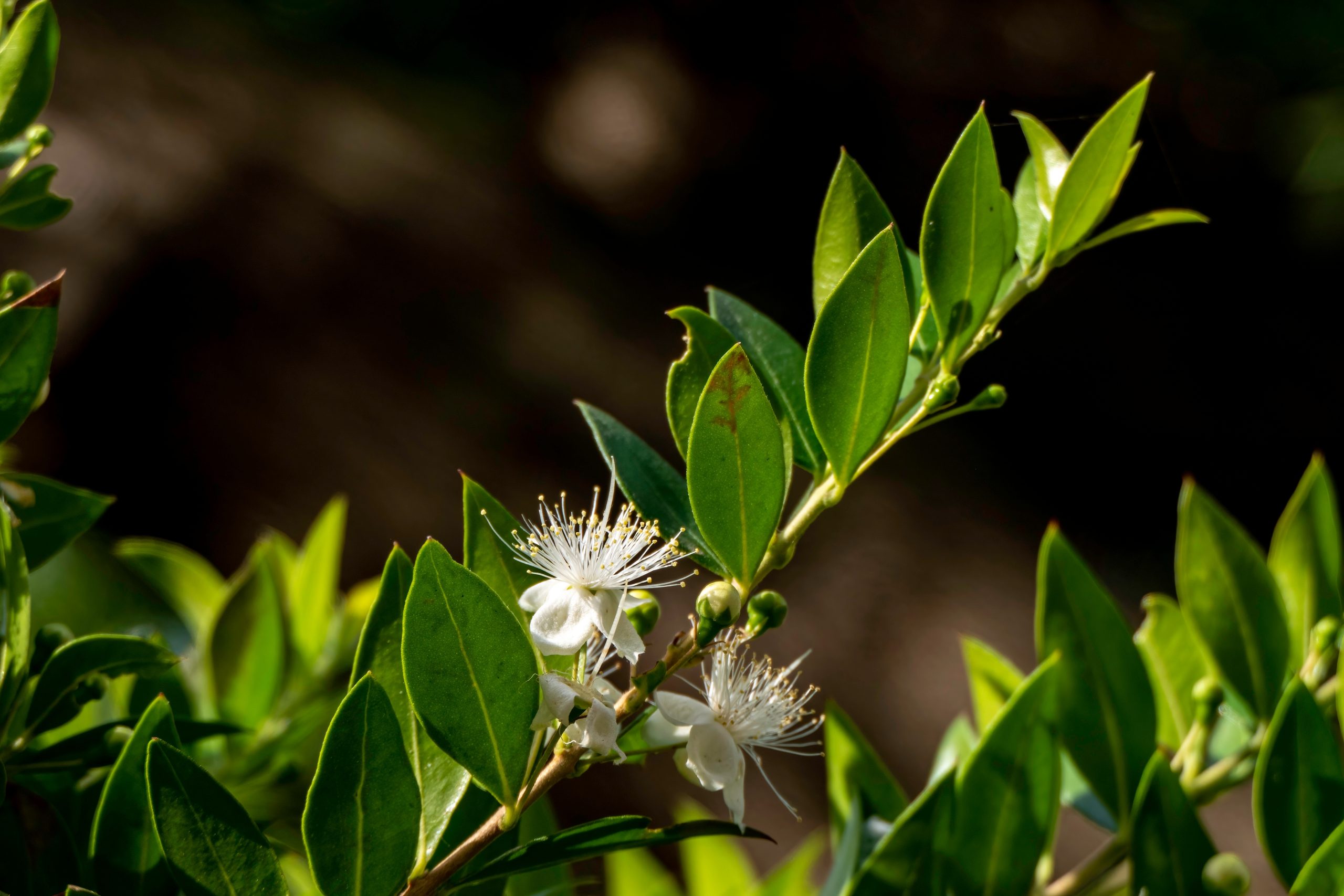
Myrtle (Myrtus communis) is an iconic shrub of Portugal and can be found in many gardens and natural landscapes in the country. Native to the Mediterranean this plant is highly cherished for its beauty and multiple uses. Everything that makes up the myrtle plant can be used, from the stem to the flowers, from the fruit and the branches, each with a particular use.
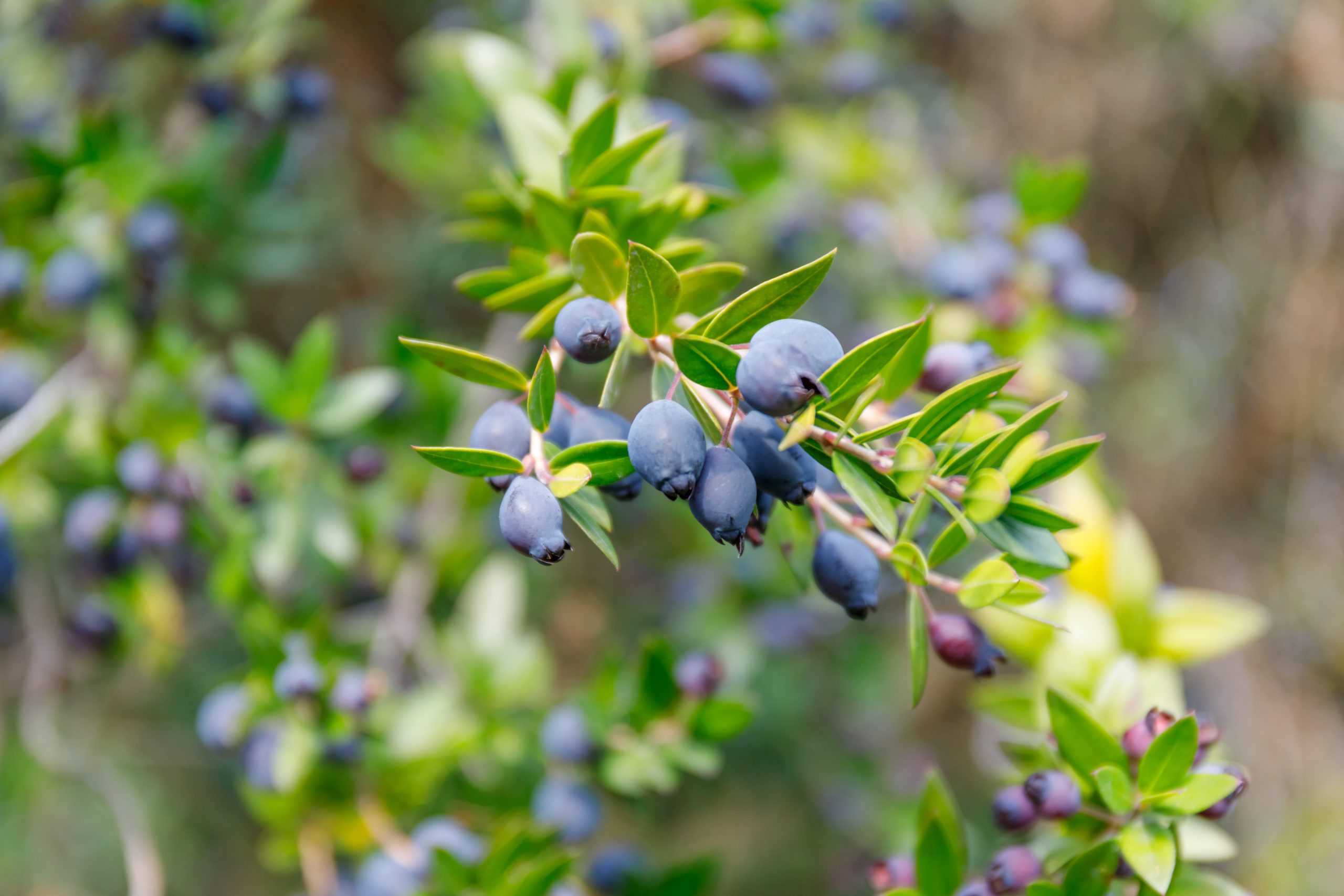
This perennial shrub belongs to the Myrtaceae family (the same family of eucalyptus), and stands out for its dark green oval foliage and its characteristic aroma, similar to that of the orange blossom, when crushed. Its whitish flowers, which appear in spring and summer, generate small dark blue berries, slightly fleshy and edible, and very similar to blueberries (Vaccinium myrtillus, a plant in the Ericaceae family).
Myrtle is also appreciated for its medicinal properties. According to popular tradition, the leaves and fruits have antiseptic, expectorant and diuretic properties that can be used in infusions to treat respiratory and digestive problems and to improve blood circulation.
In addition to its uses in medicine, myrtle has characteristics that enable it to be used as foodstuffs and to season food – flowers and leaves, green or dried, can be included in the preparation of several dishes and grilled dishes and the berries are often used to make liqueurs. From an ornamental point of view, they are used to make flower arrangements and bridal bouquets. According to popular tradition, this plant is a symbol of peace and love.
Some studies also point out the biological benefits of myrtle essential oils. In addition to its use in aromatherapy, its oil contains, for example, antibacterial properties, duly proven in extensive research conducted and dating back to the year 2010.
Furthermore, myrtle has a symbolic value in Ancient History and in Portuguese culture. Myrtle was legendary among the Greeks and Romans. In Portugal, it is often associated with religious traditions. It is also common to find it in gardens of monasteries and convents, where monks cultivated it for its medicinal and aromatic properties.
In the context of national biodiversity, myrtle plays an important role as both habitat and
foodstuff for several species of birds, insects and other animals. The nectar of its flowers, widely used in honey production, feeds many pollinating insects such as bees, which reciprocate by disseminating pollen. Berries are an important food source for some birds during winter – when food is most scarce – thus assisting the balance of ecosystems.
The myrtle is much more than just a bush. It’s a symbol of Portugal’s natural diversity, with a big historical and cultural significance and vital importance for the ecosystems where it is to be found.